Weld quality failure caused by used welded pipe machines (7)
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2023-10-16 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】When manufacturing welded pipes for used welded pipe machines, judging that the quality of the welded pipes meets the standard depends on the quality of the welds. Therefore, the quality of the weld is very important, so sometimes it is necessary to rule out the quality of the weld. We perform analyses to understand weld quality failures.
Weld quality failure caused by used welded pipe machines (7)
【概要描述】When manufacturing welded pipes for used welded pipe machines, judging that the quality of the welded pipes meets the standard depends on the quality of the welds. Therefore, the quality of the weld is very important, so sometimes it is necessary to rule out the quality of the weld. We perform analyses to understand weld quality failures.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2023-10-16 11:30
- Pvs:
When manufacturing welded pipes for used welded pipe machines, judging that the quality of the welded pipes meets the standard depends on the quality of the welds. Therefore, the quality of the weld is very important, so sometimes it is necessary to rule out the quality of the weld. We perform analyses to understand weld quality failures.
These weld quality failures will occur when the used welded pipe machines is making pipes: ① through-length lap welding. ② Periodic lap welding. ③ Open the seam. ④ Trachoma. ⑤ Peach-shaped tube. ⑥ Weld seam gnawed. ⑦Outer burr planing. ⑧ Heating. ⑨ The current is small. ⑩ Melting of induction coils and electrodes. ⑪ Fire. ⑫ "No high pressure" phenomenon. We can summarize 12 causes of weld quality failures.
Heating
There are two main forms of delivering high-frequency current to the pipe wall:
(1) the induction type. which is based on the induction coil of single-turn or multi-turn structure, which is induction welding.
(2) the contact type. which is mainly based on the movable electrode contact structure, which is contact welding.
In continuous production, the application of inductive structure is more common. Below we describe the common accidents in the heating of the tube blank.
Low current
When the current is small, the heating temperature and heating speed of the weld will be affected to varying degrees, and the quality of the weld is sometimes difficult to guarantee. In addition to insufficient output power, the reasons for the low current are mainly the following aspects in the process adjustment:
(1) The position and number of magnetic rods. In addition to the quality of the magnetic bar itself, the installation position and quantity are also very important. Generally, the front end of the magnetic bar should extend beyond the center line of the squeeze roller by more than 20 mm, and the rear end should extend beyond the induction coil or electrode by 60 mm (Figure 27).
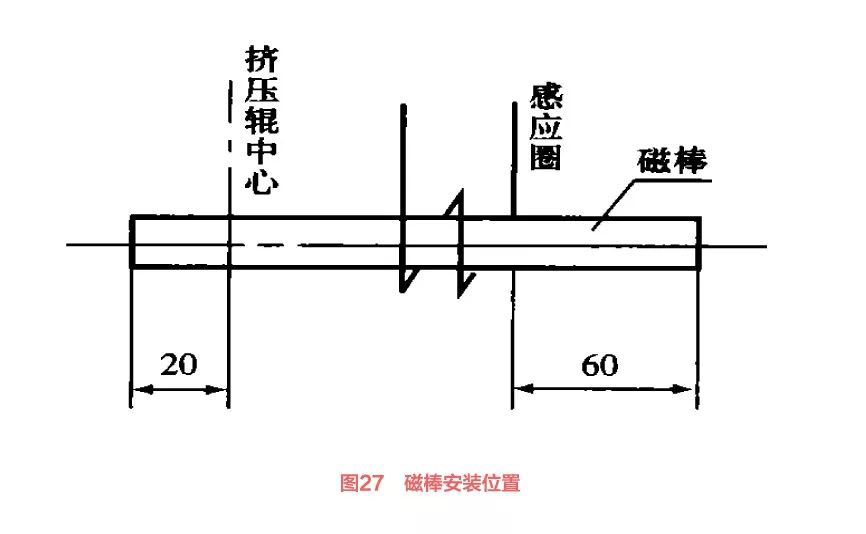
The quantity is based on the ratio of pipe diameter to magnet bar section not less than 3:1. If the above requirements cannot be met, they should be dealt with in a timely manner.
(2) Cooling effect. The magnetic bar will reduce the magnetic effect after being heated. The longer the heating time and the higher the heating temperature, the more serious the magnetic damage will be. Therefore, it is not only required that the magnetic bar itself has a better heat resistance effect, but also the external cooling must be timely. The cooling water must have both a flow rate and a flow rate, so that the magnetic bar can often work at a low temperature and prolong the service life of the magnetic bar.
(3) The position of the induction coil (or electrode). Because high-frequency current has proximity effect and skin effect, both the induction coil and the electrode should be as close as possible to the squeeze point. In addition, the gap between the induction coil and the pipe wall should preferably be controlled within 5 mm (the gap between the two electrodes should not be too large, which can generally be determined according to the width of the pipe seam, preferably 3 to 6 mm), so that it can be To ensure the heating efficiency of the weld.
(4) Weld seam control. The direction of the welding seam, the opening angle and the height position of the welding seam all have a certain influence on the size of the welding current, so when adjusting, it is necessary to ensure that the welding seam can be accurately aligned with the extrusion center, and the amount of left and right swing should not be too large. 1. 5 mm is better. The opening angle of the "V" shape of the welding seam depends on the diameter of the pipe to be produced, and is controlled between 3° and 10°, that is, the width of the pipe seam at the induction coil should not exceed 8 mm, and the width of the pipe seam at the electrode should not exceed 8 mm. 6 mm. The above can be obtained by adjusting the reduction amount of the guide roller. In addition, after the overall position of the guide roller is properly increased, the edge of the tube blank can be fully stretched, especially for the production of thin-walled tubes, which reduces edge wrinkles and stabilizes the current flow.
(5) Match. The current size and welding speed matching adjustment is a passive approach. When the current output cannot be increased, in order to ensure the quality of the weld, the only way to reduce the welding speed is to prolong the heating time of the weld to meet the temperature requirements of the weld.
The above is one of the reasons for the quality failure of the welding seam when the used welded pipe machines is making pipes, and the heating and current are small. The main reasons for the formation of heating are (1) Induction type, which is mainly induction coil with single-turn or multi-turn structure, which is induction welding. (2) The contact type is mainly based on the movable electrode contact structure, which is contact welding. There are also reasons for the formation of small currents mainly due to (1) the position and number of magnetic rods. (2) Cooling effect. (3) The position of the induction coil (or electrode). (4) Weld seam control. (5) Match.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province