Four categories of welded pipe blanks for high frequency welded pipe equipment (1)
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-05-13 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】Welded pipe blank is the raw material of high frequency welded pipe equipment to make welded pipe. Its mechanical properties and chemical composition have a profound impact on the quality of welded pipe, and its width is the first factor that determines the strength of the weld. We usually say that the width of the welded pipe blank is suitable, which refers to the width of the given thickness; the determination of the width is restricted by many factors.
Four categories of welded pipe blanks for high frequency welded pipe equipment (1)
【概要描述】Welded pipe blank is the raw material of high frequency welded pipe equipment to make welded pipe. Its mechanical properties and chemical composition have a profound impact on the quality of welded pipe, and its width is the first factor that determines the strength of the weld. We usually say that the width of the welded pipe blank is suitable, which refers to the width of the given thickness; the determination of the width is restricted by many factors.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-05-13 11:30
- Pvs:
Welded pipe blank is the raw material of high frequency welded pipe equipment to make welded pipe. Its mechanical properties and chemical composition have a profound impact on the quality of welded pipe, and its width is the first factor that determines the strength of the weld. We usually say that the width of the welded pipe blank is suitable, which refers to the width of the given thickness; the determination of the width is restricted by many factors.
This article discusses various calculation methods of tube blank width, and points out the commonalities and differences of various calculation methods and their applicable conditions. At the same time, the defects of the welded pipe blanks are divided into two categories: dominant and recessive, and the adverse effects of the defects of the welded pipe blanks on the production of welded pipes are analyzed.
Classification of welded pipe blanks:
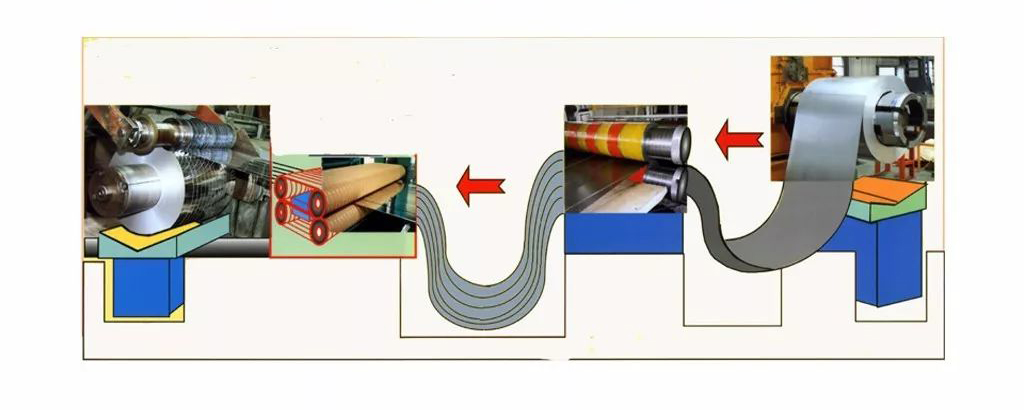
The welded pipe blanks of high frequency welded pipe equipment can be divided into four categories according to the steel type, the temperature when rolling the pipe blank, the width of the source of the welded pipe blank and the edge state of the welded pipe blank. The following introduces the welded pipe blanks classified by steel type.

Classification by steel grade
Q series welded pipe blanks: Q series welded pipe blanks are also known as ordinary carbon steel welded pipe blanks. To use ordinary carbon steel as welded pipe blank, two points need to be explained:
(1) Since ordinary carbon structural steel only has strict regulations on the chemical composition of the steel, and does not require mechanical properties, the high-frequency longitudinally welded pipes produced by ordinary carbon structural steel for high frequency welded pipe equipment are in the delivery process. In theory, the mechanical properties cannot be guaranteed.
(2) The standard is only a minimum requirement, due to the needs of market competition, and with the continuous improvement and improvement of steelmaking level, rolling technology, especially cold rolling technology and its related annealing process, finishing process, and tension leveling process, The mechanical properties of Q series welded pipe blanks have been improved a lot, and some are comparable to high-quality carbon structural steel. The mechanical properties of cold-rolled bright tubes produced by Q series cold-rolled bright annealed steel strips are not much different from those of high-quality carbon structural steel.

High-quality steel series welded pipe blanks
(1) High-quality carbon structural steel must not only ensure the chemical composition of the tube blank, but also ensure the mechanical properties of the tube blank. Therefore, the welded pipes made of high-quality carbon structural steel pipe billets are at least guaranteed in terms of mechanical properties.
(2) Affected by the Bauschinger effect, after the welded pipe blank is deformed by forming, welding extrusion and plastic deformation, indicators such as elongation and shrinkage rate will decrease, while yield strength and tensile strength will slightly decrease. rise. On the one hand, it reminds us to pay attention to the performance indicators when purchasing high-quality steel welded pipe blanks; The formed tube blank is partially stressed to prevent the Bauschinger effect from being strengthened. The Bauschinger effect manifests itself in all steel deformations, differing in degree.
Tip: Bauschinger effect: a metal that has undergone plastic deformation in a certain direction, when it is deformed in the opposite direction, its yield strength decreases significantly compared with the stress-strain in the original pre-strain direction. This phenomenon was first discovered by the German Bauschinger in 1886, and was named after him, abbreviated as BE (Bauschinger effect). This effect adversely affects the cold plastic deformation, alignment, dimensional stability and service performance of the material, adding a variable to be predicted. The research results of the Bauschinger effect given in the traditional literature usually refer to the results under the condition of axial tension and compression test, and the microscopic stress inside the material is usually the microscopic stress within the grain size range. The explanation is also based on this. However, for plastic bending from plate to tube, considerable macroscopic residual stresses are introduced, which can have an additional significant effect on the Bauschinger effect.
The method to eliminate the Bauschinger effect: perform large plastic deformation in advance, or anneal the metal material at the recovery or recrystallization temperature before the second reverse force, such as steel above 400~500℃, copper alloy At 250~270℃.
Low alloy steel series welded pipe blanks
Low alloy steel welded pipe blanks must not only ensure the chemical composition of the pipe blanks, but also must ensure high yield resistance, tensile strength and certain toughness. Mainly used to produce high strength. Impact-resistant and wear-resistant pipes, such as oil transportation pipes, coal slurry transportation pipes, transmission shaft pipes, long-span steel structure pipes, high-strength structural pipes, etc. The biggest advantage of using low-alloy steel welded pipes is the high cost performance. It can reduce the weight of meters and reduce the self-weight of components through strength replacement without reducing the strength of the components, which is particularly important for large-span steel structures.
Micro-alloyed steel series tube blank
This type of tube blank is a welded tube blank specially developed to meet the needs of some specific customers or specific uses. Mainly relying on the platform of low-alloy structural steel and high-quality structural steel, by adding some trace metals or non-metals, the tube blank and welded pipe have some special functions.
The above is one of the "steel grades" about the welded pipe blanks of high frequency welded pipe equipment. From the perspective of steel grades, it can be divided into Q series welded pipe blanks, high-quality steel series welded pipe blanks, low alloy steel series welded pipe blanks, micro-alloyed steel pipe blanks Steel series tube blanks.
Part of the content of this site comes from the Internet, this site only provides information storage, the copyright belongs to the original author, does not bear relevant legal responsibility, does not represent the views and positions of this site, if there is any infringement, please contact to delete.
More News



Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province