Weld quality failure caused by used welded pipe machines (6)
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2023-10-13 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】When manufacturing welded pipes for used welded pipe machines, judging that the quality of the welded pipes meets the standard depends on the quality of the welds. Therefore, the quality of the weld is very important, so sometimes it is necessary to rule out the quality of the weld. We perform analyses to understand weld quality failures.
Weld quality failure caused by used welded pipe machines (6)
【概要描述】When manufacturing welded pipes for used welded pipe machines, judging that the quality of the welded pipes meets the standard depends on the quality of the welds. Therefore, the quality of the weld is very important, so sometimes it is necessary to rule out the quality of the weld. We perform analyses to understand weld quality failures.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2023-10-13 11:30
- Pvs:
When manufacturing welded pipes for used welded pipe machines, judging that the quality of the welded pipes meets the standard depends on the quality of the welds. Therefore, the quality of the weld is very important, so sometimes it is necessary to rule out the quality of the weld. We perform analyses to understand weld quality failures.
These weld quality failures will occur when the used welded pipe machines is making pipes: ① through-length lap welding. ② Periodic lap welding. ③ Open the seam. ④ Trachoma. ⑤ Peach-shaped tube. ⑥ Weld seam gnawed. ⑦Outer burr planing. ⑧ Heating. ⑨ The current is small. ⑩ Melting of induction coils and electrodes. ⑪ Fire. ⑫ "No high pressure" phenomenon. We can summarize 12 causes of weld quality failures.
Weld seam gnawed
There are two forms of gnawing of welds, one is crescent-shaped scratches; the other is indentation. This kind of trauma is generally relatively minor and will not affect the quality of the weld, but the surface of the pipe is not very beautiful. Lap welds are formed when the depression marks become indented. Pinhole-type sand holes may appear in the crescent-shaped marks produced by the rupture of the upper edge of the extrusion roller hole. Therefore, we distinguish this type of accident from other scratch accidents.
(1) Crescent moon marks. The crescent-shaped scratch marks are one of the main scars on the weld, most of which are caused by the squeezing roller. Sometimes the vertical roller that forms a closed hole pattern will also cause scratches, mainly because the upper edge of the hole pattern appears. It is caused by slight cracks falling off the edge or other hard substances sticking to the edge of the hole. Especially after the extrusion roller is heated, many small cracks will be generated on the edge of the hole, and various oxidized metal impurities will be adhered, which is the cause of where the scratching problem lies. When the machine is stopped, we can use our fingers to do a touch inspection along the upper edge of the hole pattern, and repair or replace it according to the situation.
(2) Indentation. The indentation is mainly caused by the upper roll forming the closed hole pattern. Due to the characteristics of the hole structure, the bottom diameter of the upper roller is the most stressed. When the hardness of the roll is low, the wear of the pass is accelerated, and when the hardness of the roll is high, the bottom diameter of the pass is very prone to quenching cracks, and the cracked roll edge will cause many slight indentations to the weld. As the quench cracking problem increases and the reduction force increases, the indentation will become more serious. Therefore, it should be replaced in time when the hole type is found to be quenched and cracked.
Outer burr planing
Any scars that do not meet the product quality requirements formed after the outer burr is removed are called planing injuries. Although the chance of gouging is very small, it directly affects the appearance quality of the product. In order to reduce planing accidents, the cutting tools should be sharpened first, so as to improve the planing quality and save the tools. Secondly, it is necessary to ensure the stability and flexibility of the planing equipment, and to find a targeted treatment method in the event of an accident.
(1) Burning knife. Burning a knife is an accident that happens by accident. Generally, in production, the unit suddenly slows down and the heating temperature is extremely high, or the unit has just started to heat up before reaching the normal speed, which will make the high-temperature burr chips not easy to plan off the pipe surface and accumulate on the cutting edge. The blade burns out. This requires us to pay attention to the coordination and matching of operation actions and time in production, as well as the timely response of operations.
(2) The weld is uneven. The longitudinal plane of the weld seam after planing is wavy, which is called planing unevenness. If the waves are as tight as a washboard, it is usually caused by the fact that the relief angle of the cutting tool is too small or the strength of the tool bar is not enough to cause vibration. If the wave is a large wave with a long period, it generally occurs on a smaller pipe diameter. Due to its low weight, the pipe on the idler will bob up and down when planing, forming a wave shape. In addition, the instability of the tool holder will also produce a large wave jump and form a wavy planing result.
(3) Planing (scraping) partial. The welded seam after planing is an inclined plane, commonly known as planing (scraping) deviation (Figure 26).
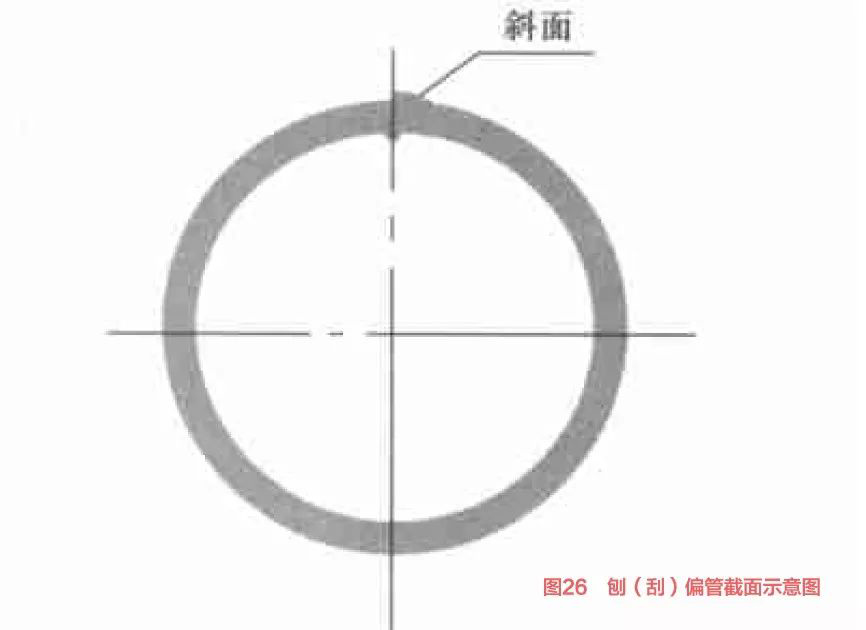
There are two main reasons for the planing (scraping) deviation.
One is that the cutting tool is installed inclined, and this problem is relatively easy to solve.
The other is caused by the pipe turning. If it is only a slight planing deviation and does not affect the welding effect, we can adjust the planing knife a little, or control the direction of the welding seam by adjusting the angle and pressure of the guide roller.
(4) Plane. Sometimes we can find that a wide and flat wound is left after the burr is removed. In fact, this has nothing to do with planing, but is caused by the "peach-shaped" pipe, which causes the welding seam to form large external burrs after extrusion, so it is necessary to replace the new extrusion roller immediately. Get good weld results and weld gouging quality.
The above is one of the reasons for the quality failure of the welding seam when the used welded pipe machines is making pipes, such as the welding seam gnawing and the external burr gouging. The main reasons for the formation of weld gnawing are (1)Crescent moon marks. (2) Indentation. There are also the main reasons for the formation of external burr planing (1) burning knife. (2) The weld is uneven. (3) Planing (scraping) partial. (4) Plane.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province