How to place the impedance and calculate the length and outer diameter of the high frequency welded pipe equipment
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2023-05-23 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】The magnet bar is an open-circuit element in the welded pipe blank of the high frequency welded pipe equipment. When it is magnetized by the magnetic field of the induction coil, the magnetic field at both ends of the magnet bar will inevitably diverge, resulting in a decrease in the effective magnetic permeability. , and thus weaken the ability of the magnetic rod to increase the impedance of the inner loop.
How to place the impedance and calculate the length and outer diameter of the high frequency welded pipe equipment
【概要描述】The magnet bar is an open-circuit element in the welded pipe blank of the high frequency welded pipe equipment. When it is magnetized by the magnetic field of the induction coil, the magnetic field at both ends of the magnet bar will inevitably diverge, resulting in a decrease in the effective magnetic permeability. , and thus weaken the ability of the magnetic rod to increase the impedance of the inner loop.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2023-05-23 11:30
- Pvs:
The magnet bar is an open-circuit element in the welded pipe blank of the high frequency welded pipe equipment. When it is magnetized by the magnetic field of the induction coil, the magnetic field at both ends of the magnet bar will inevitably diverge, resulting in a decrease in the effective magnetic permeability. , and thus weaken the ability of the magnetic rod to increase the impedance of the inner loop.
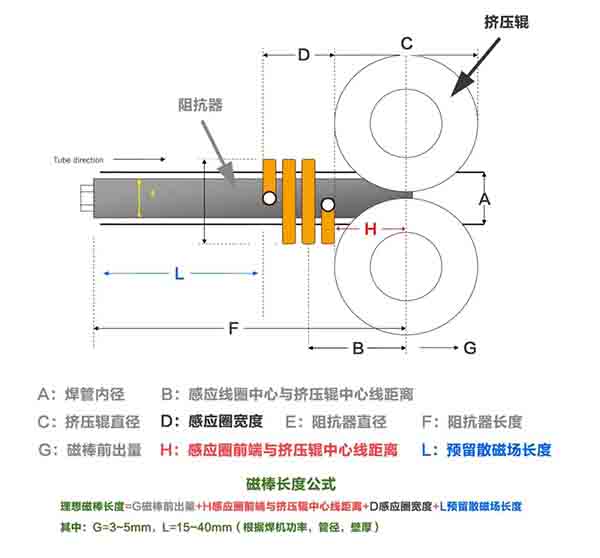
In theory and practice, in order to "eliminate" the loss of welding efficiency caused by the divergent magnetic field of the magnet bar, we usually choose the length of the magnet bar to be 15~40mm longer to reserve the length of the divergent magnetic field of the magnet bar. The larger the high-frequency power, the larger the diameter of the pipe, the thicker the pipe wall, and the larger the value of G and L; but it is not as long as possible. Too long is not only ineffective, but also increases the difficulty of placing the magnetic rod and the magnetic rod. cost of use.
The formula for the length of the magnetic rod gives the best position for placing the magnetic rod, and G should not be too long, because the welded pipe of the high frequency welded pipe equipment after welding is an irregular round pipe, and the inner diameter of the cavity will be smaller after the inner burr is added. Theoretically, it is at least 1~2mm smaller than the tube blank to be welded. If the magnetic bar is too much forward, the risk and probability of pulling the magnetic bar during the movement of the tube blank will greatly increase.
Select the outer diameter of the magnet bar
When selecting the outer diameter of the magnet bar, it should be as large as possible under the premise of ensuring the cooling effect. If the coolant pressure of the magnet bar is greater than 0.15MPa, it should be larger, otherwise it should be smaller. For details, please refer to the following formula : d=k(D-2t)
In the formula: d and D are the outer diameter of the magnetic rod and the outer diameter of the welded pipe, respectively, and t is the wall thickness. When the combined form of the magnetic rods is multiple bare rods or a cluster of bare rods, d is the maximum diameter of a bundle of magnetic rods. When the magnetic rods use insulating sleeves, it is the outer diameter of the insulating sleeves; k is the diameter of the magnetic rods. Coefficient, k=0.8~0.9, take a large value when the coolant pressure is high, take a small value when the coolant pressure is low, take a large value when using an insulating sleeve, take a large value for trimmed tube blanks, and take a large value for non-trimmed tube blanks Small value; take the large value when the butt welding joint is firm and flat, otherwise take the small value.
High frequency welded pipe equipment is equipped with magnetic rods for high frequency straight seam welded pipes. Starting from the welding principle and the actual needs of welded pipe production, pay attention to the following four points:
(1) Maximize the cross section and improve the welding efficiency.
(2) The surface area is maximized to ensure that the magnetic rod is fully cooled and dissipated.
(3) The distance between any point (referring to the radial direction) of the magnet bar and the heat dissipation surface should not exceed 20mm, so as to avoid the existence of a heat dissipation blind area, resulting in partial loss of magnetism.
(4) The geometric dimensions should be serialized, allowing users to have more choices according to the specifications of the welded pipe.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province