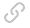Analysis of quality defects in welding section of pipe welder machine
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-04-29 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】The weld seam is the most important sign of the quality of the welded pipe and the life of the welded pipe. Therefore, the analysis and treatment of quality defects in the welding section of the pipe welder machine should be carried out around the weld. The main defects of the weld include cracks, cracks, incomplete penetration, over-burning and perforation, and dislocation of the weld.
Analysis of quality defects in welding section of pipe welder machine
【概要描述】The weld seam is the most important sign of the quality of the welded pipe and the life of the welded pipe. Therefore, the analysis and treatment of quality defects in the welding section of the pipe welder machine should be carried out around the weld. The main defects of the weld include cracks, cracks, incomplete penetration, over-burning and perforation, and dislocation of the weld.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-04-29 11:30
- Pvs:
The weld seam is the most important sign of the quality of the welded pipe and the life of the welded pipe. Therefore, the analysis and treatment of quality defects in the welding section of the pipe welder machine should be carried out around the weld. The main defects of the weld include cracks, cracks, incomplete penetration, over-burning and perforation, and dislocation of the weld.
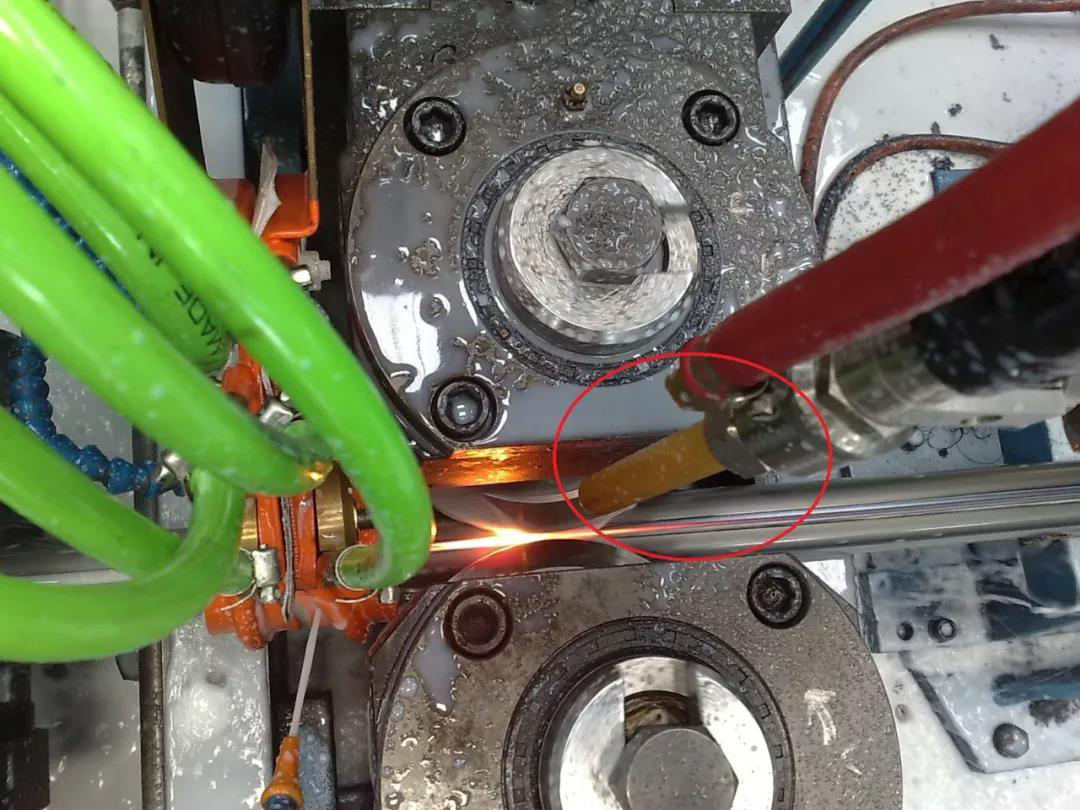
①Weld cracking:
Weld cracking includes natural cracking (including stress corrosion) and stress (additional external force) cracking.
1.Natural cracking of welds
Features: Natural cracking of the weld refers to the cracking of the weld without any additional external force at the cooling water tank, sizing machine, warehouse, etc. after the welded pipe leaves the constraint of the squeeze roller.
This kind of crack is like a zigzag, showing a grayish metallic luster. The most notable feature is that there is no external force, and there is no reason for cracking.
Causes: There are many reasons for the natural cracking of the weld, the main reasons are insufficient extrusion force, low or high welding temperature, narrow and thin tube blank, deep burr removal, butt welding surface ︿ shape Or reverse ﹀-shaped butt and high-strength tube ring caused by excessive residual tensile stress in transverse forming, etc.
Measures to prevent natural cracking of welds include:
1) Strictly inspect the raw materials and remove the hard tube blanks;
2) For different tube blanks, select a positive and stable welding process to avoid cold welding and overburning;
3) Strengthen the forming adjustment, reduce the residual stress of the forming, and realize the parallel butt joint of the welding seam.
2.Weld stress cracking
Cracked flattened welds. Including positive squashing and side squashing and cracking.
Flattening can be divided into D/3 flattening and full flattening; according to the relevant standards in my country, the weld is qualified without cracking after D/3 under positive pressure; however, from the actual use of welded pipes, most of them require full flattening without cracking. cracked. The so-called full flattening means 100% reduction to the inner wall of the tube with a clearance of 0. Full flattening can not only check the welding quality, but also check the plastic state of the tube blank.
Positive pressure weld cracking: refers to the flattening and cracking of the weld position and the force application direction on the same line. The mechanism of positive pressure internal cracking of thick-walled pipes is that the outer circular weld of the welded pipe is compressed during positive pressure, the inner circular weld is stretched, and the inner side of the weld is easily cracked.
The main reasons are: excessive deformation of the edge of the tube blank, and the welding seam is in a "︿" shape butt; the extrusion force is too small; the welding heat is insufficient; the tube blank is hard, and the weld seam is easy to crack after being stressed.
The main measures to eliminate the internal cracking of the positive pressure weld of the thick-walled pipe are: appropriately relax the first forming flat roll (referring to the W pass, edge deformation pass and comprehensive deformation pass) and closed hole roll, and at the same time increase the extrusion force, increase welding heat, and reject tube blanks that are too hard.
3.Lateral pressure weld cracking: refers to the complete cracking, partial cracking or cracking of the welding seam when the direction of the flattening force is 90° to the welding seam. The cracking mechanism of the lateral pressure weld is just the opposite of that of the positive pressure. When the lateral pressure is applied, the outer layer of the weld is in a stretched state, and the more the pressure is pressed, the smaller the curvature radius of the weld position, and the greater the tensile stress of the outer layer of the weld, the more It is easy to tear the weld and cause lateral pressure cracking.
The main adjustment measures are: increase the extrusion force and increase the welding heat; improve the forming quality, and strive to realize the parallel butt joint of the welding seam.
The elbow weld is cracked. There are two types of cracks in elbow welds: process-type cracking and strength-type cracking.
4.Process type elbow weld cracking: refers to the unequal extension or compression of the longitudinal fibers of the welded pipe due to the pipe bending process when the pipe welder machine. Causes longitudinal fibers to dislocate each other and to stagger and crack at the weakest weld. If the weld is placed on the outside of the bending arc, the tensile stress on the outside of the weld is the largest. The weld and nearby longitudinal fibers with different elongations will cause dislocation of the lattice between the structures. However, the tensile strength of the weld structure is generally lower than that of the base metal, so the longitudinal direction is prone to occur at the weakest weld. Staggered cracking and lateral fracture.
In the same way, when the weld is on the inside of the bending arc, the weld structure and its nearby metal structures will undergo longitudinal plastic compression deformation. Because of their different compressive plastic deformation capabilities, the weld is the weakest part, so the longitudinal fibers are not equal. Extrusion and flow can easily cause dislocation cracking of welds with low strength.
Therefore, in order to prevent process-type cracking of welds, in addition to optimizing the performance of the welds, on the other hand, it is recommended that the user place the welds on the bending neutral layer as much as possible, so that the welds are only subjected to a small amount of stretching during the bending process of the welded pipe. Along with the compression, the tension and compression of the fibers around the weld is also limited. Of course, if the weld is strong, performant, and soft, then no matter where the weld is placed to bend, cracking of the weld will not occur.
5.Strength type elbow weld cracking: refers to the elbow weld cracking that occurs on the premise that the chemical composition of the tube blank, the mechanical properties are good, and the weld is in the area near the neutral layer. The cause of low weld strength should be looked for. Improve weld strength.
Weld cracking caused by tube opening, flanging, taper tube, flaring, etc. To analyze the specific situation, on the premise of not exceeding the transverse elongation of the pipe, we should find out the reasons from the factors affecting the strength of the weld, and take measures to enhance the strength of the weld.
②Weld cracks
Weld cracks refer to the existence of small hair-like cracks in the weld. Most of these cracks occur on the superficial part of the weld; some can be seen at a glance, while others need to be carefully identified or even magnified to be discovered.
The reasons for the cracks are nothing more than the following:
(1) Reflow slag inclusion caused by high welding temperature.
(2) The tube blank is thin and narrow and the extrusion force is low, and some oxides are not extruded from the weld, and non-metallic inclusions are formed after cooling.
(3) There are non-penetrating lack of meat and micro-cracks on the edge of the formed tube blank.
(4) The welding seam is V-shaped butt, the superficial layer fusion tissue is loose, and the cold shrinkage stress will tear the loose tissue.
(5) The chemical composition of the edge of the tube blank is segregated and the oxide layer is thick, resulting in non-metallic inclusions with high melting point.
Most of the welded pipes with cracks can pass the hydrostatic test, but it is difficult to pass the non-destructive testing and side flattening test. Usually, the opening angle can be appropriately increased. Increase the squeezing force. Increase the soldering temperature. Measures such as improving the edge docking state are eliminated.
③ Welding seam dislocation
Weld dislocation refers to the weld formed by welding two pairs of welding surfaces not on the same plane. Weld dislocation is divided into three types: tendency weld dislocation, occasional weld dislocation and periodic weld dislocation; however, they have a common defect feature, that is, after the normal removal of external burrs, one side of the weld still remains Outer burrs. Dislocation of the weld seam will not only cause the surface of the weld seam to be unsmooth and affect the surface quality, but also reduce the welding area and reduce the strength of the weld seam.
There are many causes of weld dislocation, which are roughly as follows:
(1) The two sides of the first and second flat rollers are pressed asymmetrically;
(2) There is asymmetry, beating, non-concentricity, etc. in the extrusion roller, closed-hole roller or guide roller;
(3) The forming flat roller bearing, vertical roller bearing, guide roller bearing, squeeze roller bearing, etc. are damaged but have not been found;
(4) The thickness of the tube blank, the width and the narrow tolerance are large, S bend, sickle bend and other;
(5) The operation of the tube blank is unstable, and the left and right swing is large;
(6) There is an invisible bulge in the formed tube blank;
(7) The squeeze roll and guide roll deviate from the rolling center line seriously.
The causes of weld misalignment are complex and may be caused by a single cause, or it may be the result of a combination of several causes. The specific search should be based on the principle of first easy and then difficult, starting from the reasons that are visible and tangible, and eliminate them one by one and take corresponding measures.
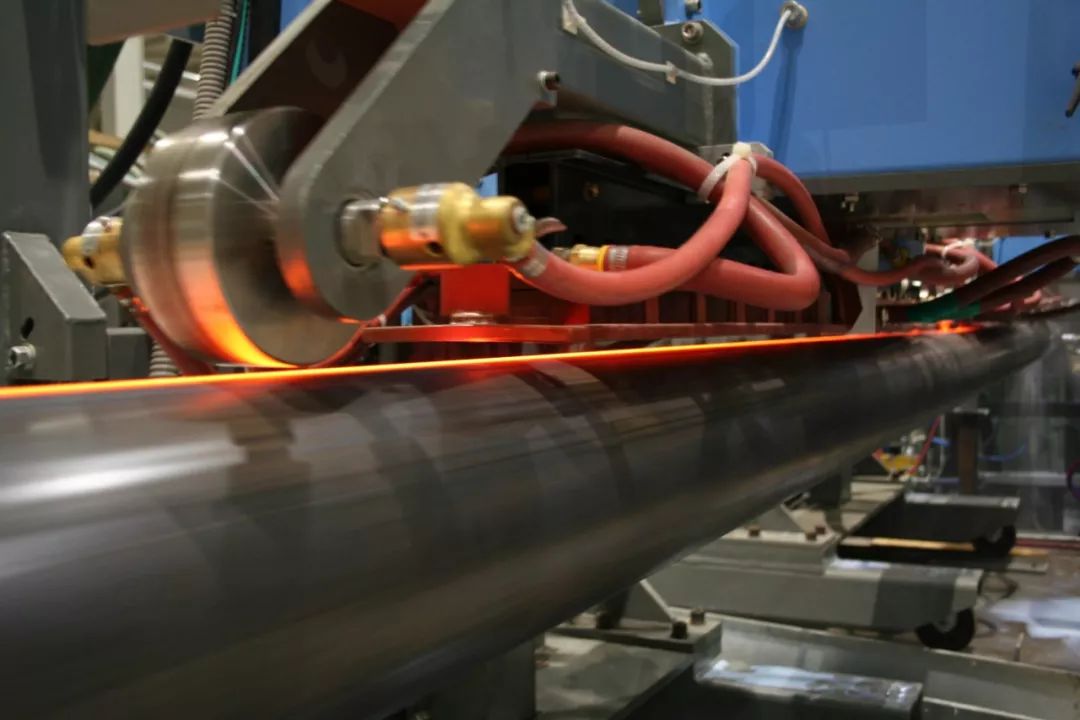

④Incomplete penetration
The notable feature of incomplete weld penetration (also known as cold welding) is that the weld has an obvious (under-penetration) or inconspicuous (slight under-penetration) groove or dark line, which mostly exists in thick-walled pipes. On the outer wall, and sometimes also on the inner wall.
The essence of incomplete penetration is that the crystallization behavior of the weld is only completed in part of the thickness direction of the tube blank, and the other parts are also heated, but the conditions for metal crystallization are not reached.
Incomplete penetration is a serious quality defect, and the reasons for incomplete penetration of the outer wall are roughly as follows:
(1) low temperature welding;
(2) Insufficient extrusion force;
(3) The welding speed is too fast;
(4) The magnet bar is demagnetized, the welding temperature is slowly lowered, and the operator is not aware of it in time;
(5) The edge of the formed tube blank is deformed and the upper edge of the extrusion roller hole is severely worn, resulting in a sharp V-shaped butt joint on the edge of the tube ring;
(6) Improper application of coolant, pour directly onto the V-shaped loop at the edge of the heating tube blank.
It should be pointed out that the dark line at the weld position is often misjudged as the scratch mark left by the removal of the outer burr.
The identification method is to wipe with sandpaper. After wiping off the surface layer, if the black line is still seen, it means that the welding is not penetrated; the second is to do the side flattening test.
The measures to exclude incomplete penetration of the outer wall are:
(1) Reduce the welding speed, increase the welding heat, and increase the extrusion force, which can be implemented individually or simultaneously;
(2) Strengthen the edge forming of the tube blank, and strive to realize the parallel butt joint of the welding edge;
(3) Replace the severely worn guide rollers and squeeze rollers in time;
(4) Check the magnet bar to ensure that it is not demagnetized;
(5) Avoid pouring the coolant directly onto the edge of the heating tube blank.
⑤ Over-burning and perforation
Overburning is a prelude to perforation, and perforation is the product of severe overburning.
Main causes of overburning and perforation:
(1)The opening angle is too small, which leads to the long liquid lintel and unstable burning;
(2)The welding speed is slow and the welding heat is too high;
(3) That the welding speed is unstable, the tube blank runs slippery, and it is prone to overburning at the moment of slippage;
(4) the welding temperature of the thin-walled tube is too high, and the opening angle is too small.
Measures to prevent burns and perforations are:
(1) Appropriately increase the opening angle to reduce welding heat input;
(2) Increase the rolling force of the flat roll and reduce the deformation force of the vertical roll to eliminate the slip of the unit;
(3) The welding process of high speed, low heat and low extrusion force should be selected for thin-walled tubes.
The above are the 5 reasons for the quality defects of the welding section of the pipe welder machine. Hope to be of some help to you. Our company has many brands and wide resources, there is always one suitable for you. You only need to inform us of your pipe manufacturing needs, and our company will provide you with used welded pipe equipment that really suits your needs.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province