Welding and rolling bottom line and sizing rolling bottom line in high frequency welded pipe machine
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-08-07 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】The rolling line of high frequency welded pipe machine is all rolls on the welded pipe unit, including leveling rolls, forming flat rolls, guide rolls, squeeze rolls, deburring idlers, calendering rolls, sizing rolls, straightening rolls and other rolls. It is also the reference line for the installation and adjustment of related auxiliary equipment such as uncoilers, spiral loopers, flying saws, conveyor rollers, etc.
Welding and rolling bottom line and sizing rolling bottom line in high frequency welded pipe machine
【概要描述】The rolling line of high frequency welded pipe machine is all rolls on the welded pipe unit, including leveling rolls, forming flat rolls, guide rolls, squeeze rolls, deburring idlers, calendering rolls, sizing rolls, straightening rolls and other rolls. It is also the reference line for the installation and adjustment of related auxiliary equipment such as uncoilers, spiral loopers, flying saws, conveyor rollers, etc.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-08-07 11:30
- Pvs:
The rolling line of high frequency welded pipe machine is all rolls on the welded pipe unit, including leveling rolls, forming flat rolls, guide rolls, squeeze rolls, deburring idlers, calendering rolls, sizing rolls, straightening rolls and other rolls. It is also the reference line for the installation and adjustment of related auxiliary equipment such as uncoilers, spiral loopers, flying saws, conveyor rollers, etc. It is the general term for the rolling bottom line and rolling center line, just like the human body. The spine plays a pivotal role in all process parameters of welded pipe production.
The following is an explanation of the bottom line of welding and rolling and the bottom line of sizing rolling in high frequency welded pipe machine.
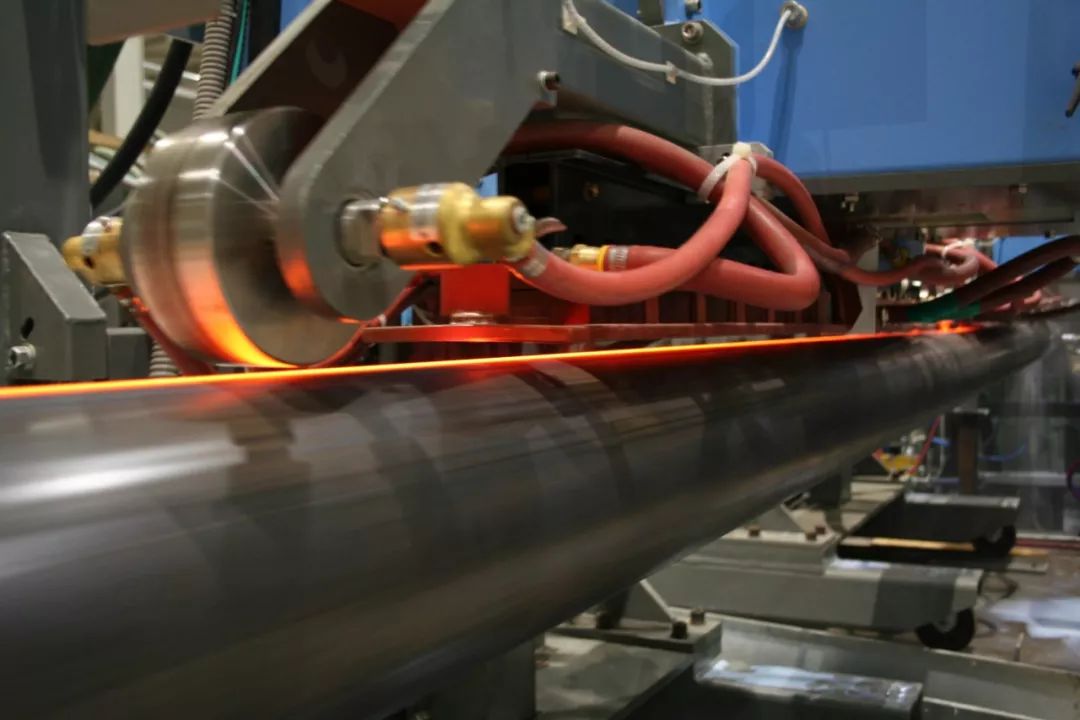

Welding and rolling bottom line
The bottom line of welding and rolling is divided into broad and narrow senses.
(1) In a broad sense, from the last forming roll to the first sizing roll, the guide roll, squeeze roll, burr idler, calender roll, cooling water jacket, etc., must be adjusted based on it. . The traditional welding and rolling bottom line is the horizontal rolling bottom line. With the continuous development of the welding theory and the continuous improvement of the production process, the rolling bottom line of the combination of the mountain and the horizontal line, the rolling bottom line of the curve and the horizontal line, etc. have appeared one after another.
Under normal circumstances, the formed tube blank is basically shaped after welding, and will not have a large negative or positive impact on the welded pipe due to the change of the rolling bottom line.
(2) The bottom line of welding and rolling in a narrow sense only guides the direction roll to the extrusion roll section. Looking at the entire molding system, this section is the end of the entire molding process, and the results and defects of the previous molding will be revealed in this area. In particular, some forming defects, through the narrow welding rolling bottom line form changes (uphill or convex arc bottom line)
, can still play a large remedial role.
Therefore, the bottom line of welding and rolling in the narrow sense should be appropriately changed according to the actual situation of the formed tube blank and in line with the bottom line of the traditional forming interval. Therefore, the bottom line of welding and rolling has a subordinate nature, and it should be flexible and flexible in the actual production process, and should not be static.
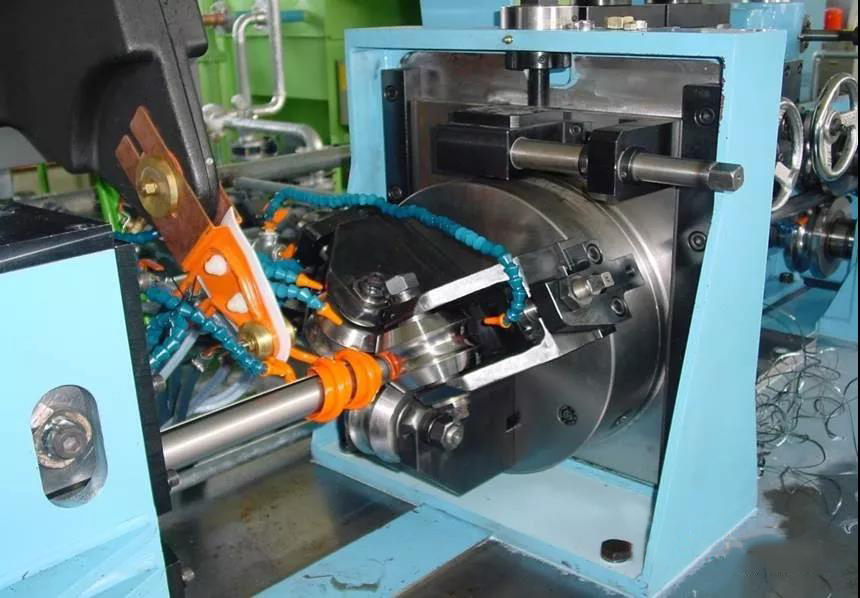

Bottom line of sizing rolling
The bottom line of sizing rolling is mostly straight. In fact, in order to reduce the longitudinal internal stress remaining in the welded pipe and reduce the difficulty of straightening, it is still necessary to consider the use of convex or "horizontal + convex" sizing rolling bottom line. "Horizontal" and "convex" are easy to understand. The bottom line of "horizontal + convex" sizing rolling means that the first and last roll passes of sizing use a horizontal rolling line, and let the second from the bottom go up. Raised. Selecting the "horizontal + convex" sizing rolling bottom line is extremely beneficial to the straightening of the welded pipe.
In the welding process of high frequency welded pipe machine, the cross-section of the welded pipe is extremely unevenly heated, and the temperature difference between the upper half of the weld position and the lower half of the base metal is huge. In this way, after the subsequent rapid cooling, the longitudinal compressive stress accumulated in the upper half of the welded pipe entering the sizing roller must be much higher than that in the lower part, resulting in an obvious uneven stress distribution. According to the principle of metal deformation, in order to straighten this welded pipe, a corresponding straightening force needs to be applied in the opposite direction of the bending. The "horizontal + convex" sizing rolling bottom line can just provide an upward straightening force, basically directional After the bent welded pipe is subjected to the directional straightening force, the upper part of the pipe is stretched and the lower part of the pipe is compressed. In this way, the original compressive stress of the upper part and the tensile stress of the lower part are reduced to different degrees, and the internal stress distribution of the welded pipe is generally equal and balanced. The welded pipe coming out of the sizing machine reaches the basic straightness, and the random straightening roller only plays the role of fine-tuning.
Operational practice has proved that if the force of the welded pipe in the sizing machine is not appropriate, the straightening effect of relying solely on the straightening head is not good and laborious.
The starting point and process goal of selecting "slightly convex" or "horizontal + convex" sizing rolling bottom line are the same, the difference is: the amount of convexity of "slightly convex" is distributed among all the sizing rolls in all passes. Since it is a small amount and needs to be distributed to each pass, it is difficult to operate and grasp it; and "horizontal + convex" only needs to reflect the convex amount on one sizing roller, which is more convenient and flexible to operate. concise.
In addition, if the high frequency welded pipe machine adopts the bottom line of downhill forming, the extension of the bottom of the forming tube blank will be slightly more than that of the middle and upper parts, so the welded pipe will have a tendency of upward warping or upward warping. more necessary.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province