Summarize the opening angle of the pipe welder machine
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-05-07 11:30
- Pvs:
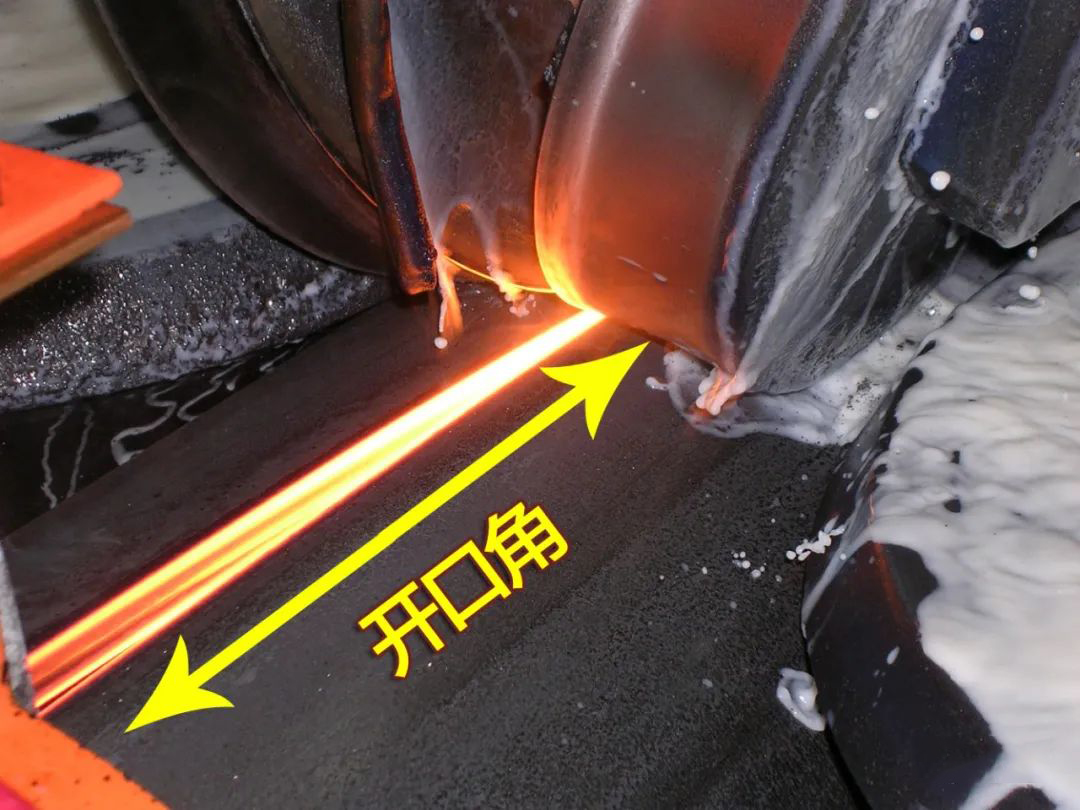
【概要描述】The opening angle of the pipe welder machine means that under the action of the extrusion force of the extrusion roller and the elastic stress related to the thickness of the guide ring, the two edges of the pipe blank take the focus of the center line of the extrusion roller as the pole and the pipe blank to be welded. The two edges are the angle formed by an effective length of the ray, as shown in Figure 1.
Summarize the opening angle of the pipe welder machine
【概要描述】The opening angle of the pipe welder machine means that under the action of the extrusion force of the extrusion roller and the elastic stress related to the thickness of the guide ring, the two edges of the pipe blank take the focus of the center line of the extrusion roller as the pole and the pipe blank to be welded. The two edges are the angle formed by an effective length of the ray, as shown in Figure 1.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-05-07 11:30
- Pvs:
The opening angle of the pipe welder machine means that under the action of the extrusion force of the extrusion roller and the elastic stress related to the thickness of the guide ring, the two edges of the pipe blank take the focus of the center line of the extrusion roller as the pole and the pipe blank to be welded. The two edges are the angle formed by an effective length of the ray, as shown in Figure 1.

The opening angle has three connotations:
(1) The formation process of the opening angle is more complicated. It is closely related to the extrusion roll, the edge of the tube blank, the thickness of the guide ring, the distance between the extrusion roll and the guide roll, and the material of the tube blank. Any change in any of these aspects will affect the opening angle.
(2) The opening angle is a dynamically changing quantity.If the thickness of the guide ring is simply used as the parameter, the change rule is that as the thickness of the guide ring becomes thinner (the guide ring needs to be replaced), the opening angle gradually decreases; when the guide ring is replaced, the opening angle increases suddenly, so the Change has the characteristics of transient and sudden change.
(3) Effective control length of opening angle. From the definition of the opening angle and Figure 1, it can be seen that the forming interval of the opening angle is only within the range determined by the edge ray of the tube blank.
Factors that affect the opening angle
The opening angle is one of the most sensitive elements in the welding elements of many pipe welder machine. The size of the opening angle directly affects the welding heat, welding speed and weld strength, which involves a wide range of aspects, and there are at least 6 direct factors that affect the opening angle.
(1) Squeeze roll hole radius. According to the welded pipe production process, the radius of the extrusion roll pass is always smaller than the radius R of the open cylindrical tube to be welded. In this way, different extrusion roll passes (R1≠R2) produce different first force points on the edge of the tube blank. , thereby affecting the position and opening angle of the edge of the tube blank. When the opening angle becomes smaller, the actual apex of the edge of the heating tube blank will inevitably be advanced, and defects such as over-burning and weld perforation are easy to occur. For the same kind of tube, the opening angle will decrease sharply as the radius of the extrusion roller hole becomes smaller, resulting in the actual convergence point of the edge of the tube blank moving forward, that is, the principle of the center line of the extrusion roller, and a series of welding process parameters such as extrusion. Force, input heat, resistor position, welding speed, etc. have a significant impact.
(2) The outer diameter of the squeeze roller. Welded pipes of the same specification, different outer diameters of extrusion rollers, and the first force point of the hole pattern to the pipe blank are different. The extrusion roller with a larger outer diameter touches the tube blank earlier than the extrusion roller with a smaller outer diameter, which in turn affects the opening angle and the position of the actual meeting point.
(3) Thickness of guide ring. The thickness of the guide ring is proportional to the tangent of the opening angle, the thicker the ring, the larger the opening angle; conversely, the thinner the ring, the smaller the opening angle.
(4) The tube blank springs back. The tube blank has high strength and high hardness (such as high-strength steel), and the edge of the tube blank has a large rebound in the elastic deformation zone, and the opening of the tube blank will exceed the thickness of the roll ring, resulting in a fact that the opening angle is larger than the theoretical opening angle.
(5) The height of the tube blank entering the extrusion roller. Since the size of the open tube is larger than the size of the pass of the squeeze roll, when the guide roll and squeeze roll are adjusted according to the horizontal rolling bottom line, the edge of the tube blank is higher than the upper edge of the pass of the squeeze roll (D guide - D squeeze) mm, This causes the pressure point on the extrusion roll pass to be pressed to the edge of the tube blank in advance, and thus reduces the opening angle; the higher the higher, the more pronounced the reduction.
In particular, this can be considered as one of the measures to control the opening angle. If the opening angle of the guide ring is too large after the new guide ring is replaced, the guide roller should be properly increased as a whole; on the contrary, when the guide ring is seriously worn and the opening angle is small, the guide roller can be appropriately lowered as a whole.
(6) The wall thickness of the tube blank. The thick-walled tube plus the deformation blind area can easily form inner and outer opening angles with the same size but different apex (convergence) positions. According to the principle of proximity effect of high-frequency current, the temperature near the inner opening angle of the tube must be higher than the outer opening angle. The temperature at the opening corner makes the welded pipe process at a loss.
(7) Roll gap. The roll gap including the guide roll and the squeeze roll affects the opening angle to varying degrees.
How to adjust the opening angle
There are roughly four ways to adjust the opening angle of the pipe welder machine:
(1) Roll gap adjustment method. Control the opening angle by increasing or decreasing the gap between the guide rollers
(2) Compensation hole type wear method. When the hole pattern and guide ring are worn, the guide upper roller can be pressed down appropriately to reduce the opening angle. When the new guide ring is replaced, the opening angle will return to the maximum at once.
(3) Guide roller hole type adjustment method. It is to configure 2~3 kinds of guide rings with different thicknesses and guide rollers with different hole sizes for each outer diameter of the welded pipe, which can be selected for the production of welded pipes.
(4) Relative height adjustment method. Refers to the center of the squeeze roller as the benchmark, the overall appropriate adjustment of the guide roller or lower, to achieve the purpose of reducing or increasing the opening angle.
Adjustment principle of opening angle
When adjusting the opening angle of the pipe welder machine, the following 4 basic principles should be followed:
(1) The principle of wall thickness. It means that the opening angle should be reduced as much as possible when producing thick-walled pipes, and the opening angle should be appropriately increased when producing thin-walled pipes.
(2) The principle of nature. That is, after the natural wear of the guide ring and the hole pattern, the guide roller is pressed down in stages, so that the opening angle will be reduced accordingly; after the new guide ring is replaced, the opening angle should be restored to the original state.
(3) The principle of micro deformation. Theoretically speaking, the guide roller does not undertake the task of deformation of the tube blank; however, from the actual needs of stabilizing the opening angle, it is necessary for the guide roller to undertake the slight deformation that is limited to controlling springback.
(4) The principle of efficiency. In order to improve the power utilization efficiency and production efficiency, the opening angle must be adjusted as small as possible when the process conditions allow.
Part of the content of this site comes from the Internet, this site only provides information storage, the copyright belongs to the original author, does not bear relevant legal responsibility, does not represent the views and positions of this site, if there is any infringement, please contact to delete.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province