On-line heat treatment weld process and air cooling length of used roll forming machine
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-05-10 11:30
- Pvs:
【概要描述】There are three types of welding seam processes for online heat treatment of used roll forming machine: annealing, normalizing and quenching + tempering. Manufacturers only need to choose the corresponding process according to the pipe products and customer needs.
On-line heat treatment weld process and air cooling length of used roll forming machine
【概要描述】There are three types of welding seam processes for online heat treatment of used roll forming machine: annealing, normalizing and quenching + tempering. Manufacturers only need to choose the corresponding process according to the pipe products and customer needs.
- Sort:Information
- Auth:
- Source:
- Release time:2022-05-10 11:30
- Pvs:
There are three types of welding seam processes for online heat treatment of used roll forming machine: annealing, normalizing and quenching + tempering. Manufacturers only need to choose the corresponding process according to the pipe products and customer needs.
Annealed (A)
The function of on-line annealing of welds is to reduce the hardness of welds and heat-affected zones, improve plasticity, refine grains, and eliminate residual stress.
The commonly used annealing process is: heating the weld and the heat-affected zone to 640~680°C, then air-cooling to about 350°C, and then cooling to room temperature by spraying water or bathing.
Normalizing (N)
The purpose of normalizing is to eliminate the coarse grains in the weld area, refine and uniform the weld structure, and improve the mechanical properties of the used roll forming machine weld.
The process route is: after heating the weld area to 30~50°C above the Ac3 line, that is, 920°C~950°C, air-cooled to 350°C, and then forcedly cooled with coolant.
Remarks: Heat treatment Ac3 is a temperature code, A stands for critical point, c stands for heating. Different carbon content steel grades and different alloying element content steel grades have different heat treatment Ac3. On the iron-carbon phase diagram, people name the temperature of 230°C (Curie point of cementite) as A0, 727°C as A1 (PSK line of iron-carbon phase diagram), and 770°C (iron-carbon phase diagram) for the convenience of application. The Curie point of the element body, the magnetic transition point) is A2, 727~912°C is A3 (GS line of the iron-carbon phase diagram), and 1394~1495°C is A4 (the NJ line above the iron-carbon phase diagram)

Quenching + Tempering (Q+T)
The function is to reduce the hardness of the weld area, improve the plasticity and toughness, reduce the internal stress, and obtain good comprehensive mechanical properties.
The heat treatment process is as follows: after heating the weld area to the normalizing temperature, spray water for quenching, then heat it to the tempering temperature (540 ~ 650°C), and then start to add water for forced cooling after air cooling to 350°C.
The latter two heat treatment processes are mostly used for high-grade steel oil and gas pipes, as well as high-grade welded pipes according to process requirements.
Air cooling length
After the welding seam is heated by medium frequency induction, the air cooling speed should not be too fast, otherwise it will affect the structure and performance of the welding seam area. From the point of view of heat treatment, a longer holding time is conducive to the homogenization of alloy elements and the homogenization of the weld structure, and the comprehensive mechanical properties such as plasticity and toughness of the weld area are also better. However, due to the constraints of the process layout and the economy of the plant land, it is impossible to keep the air-cooling section very long, which requires an analysis of the factors affecting the air-cooling effect, and a balance point between the two to ensure the welding after heat treatment. The joint has good comprehensive mechanical properties and can use the site more economically. At present, the air cooling length of the used roll forming machine is mostly selected between 50 and 60m. From the perspective of production practice, it can basically meet the needs of normal production of welded pipes and on-line heat treatment of welded seams.
Another way to determine the air cooling length L is to determine the air cooling length according to the following formula according to the type of heat treatment, welding speed and air cooling speed, etc.
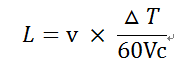
Formula:
L——the length of air cooling required after heat treatment of the weld, m;
v——the welding speed of the unit, M/min;
△T——The difference between the heat treatment temperature of the weld and the final cooling temperature, °C;
Vc - cooling rate, °C/s.
Part of the content of this site comes from the Internet, this site only provides information storage, the copyright belongs to the original author, does not assume relevant legal responsibility, does not represent the views and positions of this site, if there is any infringement, please contact to delete.
More News

Time of issue : 2023-10-31

Time of issue : 2023-10-28

Time of issue : 2023-10-25

Time of issue : 2023-10-22
Wechat: 13392281699
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Company address:No. A99, East Lecong Avenue, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Recommendation
Online Inquiry
LINK
Contact Us
Tel (wechat): 13336487288
Wechat:+86 13336487288
WhatsApp:+86 13336487288
Email: zty@usedpipemill.com
Address: No. A99, Lecong Avenue East, Lecong Town, Foshan City, Guangdong Province